Services
Our services Machakos Imaging Centre offers:
MRI
MRI uses a large magnet and radio waves to look at organs and structures inside your body. MRIs are very useful for examining the brain and spinal cord.
CT SCAN
CT Scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that combines the use of x-rays with computer technology to produce cross-sectional images (“slices”) of the body.
ULTRASOUND
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to view inside the body. There is no ionizing radiation exposure associated with ultrasound imaging.
FLOUROSCOPY
Fluoroscopy is a medical imaging that shows a continuous X-ray image on a monitor, much like an X-ray movie. The image is transmitted to a monitor so the movement of a body part or of an instrument or contrast agent through the body can be seen in detail.
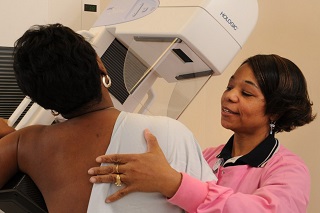
MAMMOGRAPHY
Digital Mammography is a specialized medical imaging that uses low-dose x-rays system to see inside the breasts. Mammography exam (mammogram) are used as a screening tool to detect early breast cancer in women experiencing no symptoms.
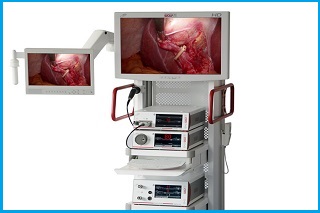
ENDOSCOPY
Endoscopy is a nonsurgical procedure used to examine a person’s digestive tract. Using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a light and camera attached to it, your doctor can view pictures of your digestive tract on a color TV monitor.
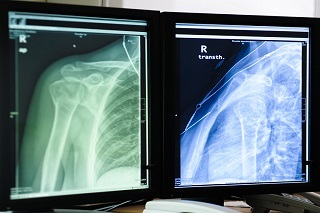
DIGITAL X-RAY
Digital X-ray involves exposing the part of the body that is being examined to a small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body. It also is used to diagnose fractures and other abnormalities of bones, joint conditions, and causes of abdominal pain.
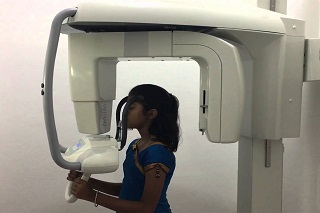
OPG
An Orthopantomogram (OPG) is a panoramic or wide view x-ray of the lower face, which displays all the teeth of the upper and lower jaw on a single film. It demonstrates the number, position and growth of all the teeth including those that have not yet surfaced or erupted.
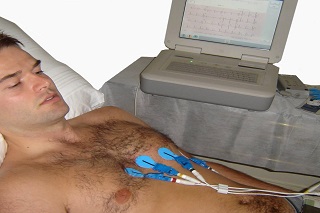
ECG
Electrocardiography is a painless procedure in which the heart’s electrical impulses are amplified and recorded to check for signs of heart disease. The impulses are recorded through small electrode patches attached to chest, arms, and legs.
More offered services
Echocardiagraphy
Echocardiography is a test that uses sound waves to produce live images of your heart. The image is called an echocardiogram. This test allows your doctor to monitor how your heart and its valves are functioning. The images can help them get information about: blood clots in the heart chambers.
Electroencephalogram
An electroencephalogram (EEG) test detects electrical activity in your brain using small, flat metal discs (electrodes) attached to your scalp. This activity shows up as wavy lines on an EEG recording. An EEG is one of the main diagnostic tests for epilepsy. An EEG may also play a role in diagnosing other brain disorders.
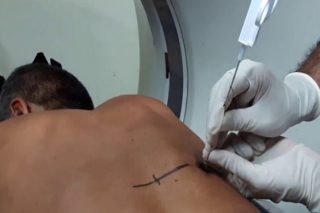
CT Guided Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of tissue from any part of the body in order to examine it for disease. Some biopsies may remove a small tissue sample with a needle while others may surgically remove a suspicious nodule or lump. The type of procedure used to perform a biopsy will depend on the location of the tissue that needs to be examined.
Biopsies may be performed using imaging guidance—such as ultrasound, x-ray, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)—to determine exactly where to place a needle through the skin to the area of the abnormality. Biopsies are most often done to look for cancer.
A biopsy might be recommended whenever:
- A mammogram shows a lump or mass, indicating the possibility of breast cancer.
- A mole on the skin has changed shape recently and melanoma is possible.
- A person has chronic hepatitis and it’s important to know if cirrhosis is present.
Call us now if you are in a medical imaging emergency need, we will reply swiftly.